ATTENTION! This article is written solely for technical and informational purposes and therefore does not constitute / replace a medical prescription.
Anadrol (Oxymetholone – Oxymetholone) is perhaps second only in importance to Dianabol (Methandrostenolone) among oral anabolic steroids for mass used in bodybuilding. This is due to its undoubted effectiveness. Like Dianabol, Anadrol has almost absolute non-affinity for the androgen receptor (AR). Thus, much of the anabolic effect it claims to arise is through non-AR mediated effects.
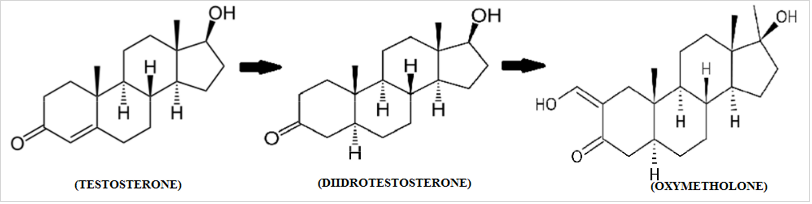
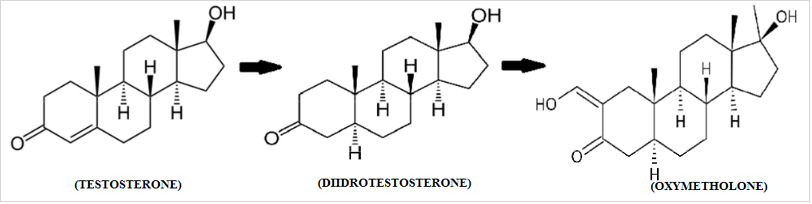
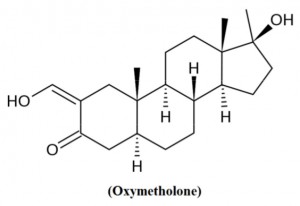 The active ingredient in Anadrol is Oxymetholone or Oxymetholone [ 17β-hydroxy-2-hydroxymethylidene-17α-methyl-3-androstanone ], which was sold in the USA under the name Anadrol 50 (Anadrol is a registered trademark of Unimed Pharmaceuticals in the US and other countries). It is an AAS, manufactured by Syntex in 1961 and originally marketed for the treatment of plastic anemia, based on the expressed erythropoietic properties of the molecule. After retirement from erythropoietin (EPO) and related drugs, oxymetholone has recently found use in the treatment of AIDS patients. Some studies in fact highlight its ability to actively counteract conditions of severe physical impairment (cachexia or wasting syndrome). It is clear that today this molecule largely retains its popularity among bodybuilders due to its anabolic properties at the muscle level, which is associated with a strong ability to stimulate the immune system.
The active ingredient in Anadrol is Oxymetholone or Oxymetholone [ 17β-hydroxy-2-hydroxymethylidene-17α-methyl-3-androstanone ], which was sold in the USA under the name Anadrol 50 (Anadrol is a registered trademark of Unimed Pharmaceuticals in the US and other countries). It is an AAS, manufactured by Syntex in 1961 and originally marketed for the treatment of plastic anemia, based on the expressed erythropoietic properties of the molecule. After retirement from erythropoietin (EPO) and related drugs, oxymetholone has recently found use in the treatment of AIDS patients. Some studies in fact highlight its ability to actively counteract conditions of severe physical impairment (cachexia or wasting syndrome). It is clear that today this molecule largely retains its popularity among bodybuilders due to its anabolic properties at the muscle level, which is associated with a strong ability to stimulate the immune system.
The structure of this molecule, as can be seen, derives from the structure of DHT, from which it differs only in two aspects:
- Methylation in C-17, which ensures its oral bioavailability, which leads to pronounced toxicity to the liver: however, despite its poor reputation in this regard, Oxymetholone (mg per mg) is no more toxic than any other C-17-alpha alkylate. However, its “in practice” toxicity increases due to the high doses in which it is usually used;
this custom is defined by another characteristic that distinguishes it from DHT, namely:
- The presence of the C-2 hydroxymethyl group , which in turn determines, as stated above:
- Almost absolute lack of affinity for androgen receptors (AR), in contrast to the ability to bind, probably also in a non-receptor way with the target site, which allows for effective administration, in particular, doses and increased, without confirmation of the so-called ” receptor saturation phenomena “; it has recently been hypothesized that oxymetholone (like possibly other AAS) binds to the non-genomic portion of androgen receptors or other steroid receptors, an event that has not yet been fully verified.
- The increase in anabolic strength (stabilizing the ketone at C-3) that makes oxymetholone, even only mg per mg, a respectable anabolic (anabolic value 320 versus methyltestosterone 100 and therefore about 450 versus testosterone). li>
- The ability of a molecule to bind to an estrogen receptor, rendering the antiestrogenic action of aromatase inhibitors ineffective. However, estrogenic activity is also mediated by the molecule’s ability to reduce SHBG, which makes the compound even more estrogenic when co-administered with aromatizing anabolic steroids and SHBG-like drugs such as usually testosterone or even boldenone. This action against SHBG, however, peaks at 50 mg / day with about 40% suppression and decreases to about 25% at 100 mg / day;
- Very low affinity for SHBG;
- The ability to raise the cortisol binding protein, thereby decreasing its biologically active part.
Another special characteristic of oxymetholone is its susceptibility to removal of small amounts of the methyl group at C-2, which determines its conversion to 17-alpha-methyl DHT ( 17AMDHT ), which determines, based on its strong affinity for SHBG, further bioavailability of co-administered AAS such as testosterone. 17AMDHT measures the residual androgenic effect of oxymetholone, which, mg per mg, is quite modest (45 relative to methyltestosterone base 100) with an excellent (despite popular belief) benefit / risk ratio for female athletes (10/1).
Finally, oxymetholone causes a certain inhibition of the enzyme 11-beta-hydroxylase , followed by water retention, which is complemented by the effect caused by its estrogenic effect: this is partially a beneficial effect, especially if oxymetholone is supplemented with potassium, since cellular overhydration increases protein synthesis. Obviously, after stopping the use of the product, there will be a decrease in muscle volume.
This is also due to a decrease in the effectiveness of the product depending on time and method: in fact, the greatest results are found within the first 10 weeks. reduce in the next to twenty; it may also be due to a negative cyclical effect that causes an increase in ACTH activity / production in response to an initial decrease in free cortisol.
Combining Anadrol with AAS such as Trenbolone, Anavar or Primobolan has a strong synergistic effect. In practice, oxymetholone can be associated with AAS, PH and DS type AR. The co-administration of Anadrol with Dianabol is not recommended, since the benefit / risk ratio is very unfavorable (excessive hepatotoxicity and excessive water retention, followed by a dangerous increase in blood pressure).
Contrary to the expectations of many bodybuilders, oxymetholone can be weak in terms of side effects when the flavored AAS is not given at the same time. However, when oxymetholone is used on a cycle in which estrogen levels are high, it is known to worsen estrogen-dependent symptoms. These symptoms are due to its estrogen-progestogenic effect, which produces the typical effects of a further increase in estrogen caused by the enzyme aromatase or an increase in prolactin. There is some indirect evidence that the problem may be mainly related to progestogenic activity: in some cases, the simultaneous use of moderate doses of Winstrol (stanozolol), which has an antiprogestogenic effect, can avoid this problem. Some even report using Dostinex (Cabergoline), which reduces prolactin, to get a cure for the problem. It is through the use of oxymetholone in high estrogen conditions that Anadrol has gained the reputation of being a “heavy” AAS. For example, when used in combination with high doses of testosterone without an aromatase inhibitor, oxymetholone becomes difficult to control due to the deterioration of estrogen and progestogen activity.
Most users do not consider it an AAS, which is difficult to treat. cope when there are no accompanying problems with high estrogen levels. Regardless of whether oxymetholone aromatizes as it is a molecule derived from DHT, in those who have already developed Anadrol gynecomastia, due to its previously reported effects, it can be an aggravating factor, even with estrogen levels kept at normal levels. It can also be a causative agent.
For those with gynecomastia problems who are thinking about using Anadrol and are unsure of their response to the molecule, rather than relying solely on Cabergoline (By the way, you can see more details about Cabergoline on the website https://steroidsbuyonline.com/store/post-cycle-therapy/cabergoline/ and / or Winstrol to avoid progestogenic effects, and especially if they use a flavored AAS, desirably bind the cycle to an aromatase inhibitor and / or a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) such as nolvadex. Those who do not have pre-existing gynecomastia and have normal estrogen levels (and are not susceptible to subjects) using Anadrol will not exhibit excessive estrogenic side effects over the course of a cycle (dose and time dependent). The above protective measures are usually optional.
For a first-time user of oxymetholone, it is not unusual to obtain satisfactory results using only one cycle of this molecule taken separately; but the most effective use of oxymetholone is combined with an AAS, usually AR. Typical use is 50-150 mg / day to be divided into two to three doses per day. While higher daily doses can produce linear anabolic effects, the effects on the liver can be troubling, especially if you exceed four / six weeks of continuous use. Sudden increases in weight and strength have occurred while using oxymetholone: on average, an athlete can increase weight by even 7-11 kg in the first three weeks of use. But it’s good that the reader understands that most of the weight gained was due to water retention. Users also reported strong increases in strength and recovery, as well as aggression (which, if focused only on training, was considered positive). Due to its ability to retain fluids even at joint level, athlete users reported that when using oxymetholone, especially hard workouts were free of joint pain, and recovery between sets was incredible (also recovery between workouts was halved). Anadrol has also been used in pre-race by experienced athletes associated with Nolvadex and a diuretic antagonist.
When used alone, testosterone production is not completely suppressed, as there appears to be no indication of abnormally low estrogen levels as occurs when endogenous testosterone production is completely suppressed. In combination with a non-flavored injectable AAS, it is also advisable to use a certain amount of testosterone or other flavored steroids, or, alternatively, testosterone can be supplied endogenously through the use of low doses of hCG. If injectable testosterone is used, even a dose of 100 mg / week is sufficient for this purpose. It should also be said that if used alone, maintaining mass after a cycle becomes a dream, if you do not inject AAS with such strong anabolic properties as Trenbolone, Winstrol Depo, Deca Durabolin, Boldenone, Oxandrolone, etc.
As mentioned, oxymetholone is a C-17-alkylated molecule and is toxic to the liver. It is recommended that you limit your Anadrol use to no more than six consecutive weeks before taking a break, which will allow you to restore altered transaminase values.
As mentioned in my previous article, Anadrol has been clinically shown to have low virilization at doses well in excess of the doses required for the weight / strength cycle of an athlete who is involved in bodybuilding or weight lifting. The total dose of 25 mg / day is only half the minimum dose used in medicine, but it is extremely effective in stimulating muscle anabolism in women. Even 12.5 mg / day can be very effective. As with any oral AAS used by athletes, split doses throughout the day are likely safer than single doses for a given total dose per day to maintain constant levels of the molecule for twenty-four hours versus peaks followed by sharp falls, the active life of oxymetholone is about 16 hours.
For women, it is also ideally associated with ostarine, which is a potent RA with few side effects.
To protect against possible side effects of oxymetholone in the liver, the use of silymarin, tudki and NAC is strongly recommended. If an athlete decides to reap the benefits of sustained efficacy at high doses of oxymetholone, over 200 mg / day, with all the risks involved, a strong supplemental supplementation of N-ademethionine (Samyr) and reduced glutathione (Tad) levels is needed. We also recommend using high doses of omega-3 and niacin to control blood lipids, which may undergo negative changes (increase in LDL and decrease in HDL, increase in triglycerides). Because Anadrol stimulates the production of red blood cells (erythrocytes), people with excessive coagulation problems, or if the high dose of Omega 3 is insufficient to maintain blood flow at acceptable levels, cardio aspirin (100 mg / day) is recommended.
Hopefully once again it was helpful to clarify some of the concepts behind chemistry applied to bodybuilding.